Endoscopic Spine Surgery is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat conditions like herniated discs, spinal stenosis, and sciatica. Through small incisions, an endoscope (a tiny camera) and specialized instruments are used to address spinal issues with precision. This technique minimizes muscle damage, reduces blood loss, and typically results in less post-operative pain. Advantages include smaller scars, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times. Patients often return to normal activities within weeks. At Specialist Minimally Invasive Spine Surgeon's clinic, we provide expert, compassionate spine care to ensure optimal recovery and improved quality of life for our patients.
Back pain can be debilitating, affecting your mobility, daily activities, and overall quality of life. However, undergoing traditional open spine surgery isn't the only solution. At S.P.I.N.E. Center Chesterfield, Dr. Amit Bhandarkar specializes in endoscopic spine surgery, a cutting-edge, minimally invasive technique that offers faster recovery, minimal discomfort, and highly effective results.
With same-day discharge, a return to work within two weeks, and higher success rates (80-90%), endoscopic spine surgery is revolutionizing spinal care, helping patients regain their active lives with minimal disruption.
Unlike traditional open spine surgery, which involves large incisions, muscle dissection, and extended recovery times, endoscopic spine surgery provides several advantages:
Endoscopic spine surgery is a state-of-the-art, minimally invasive technique that uses an endoscope—a small, tube-like camera—to visualize and treat spinal conditions with high precision. Here's how the procedure works:
This advanced technique allows for minimal blood loss, reduced trauma, and a faster return to normal activities compared to conventional spine surgeries.
If you're considering endoscopic spine surgery, here's what to expect throughout the process:
During your visit to S.P.I.N.E. Center Chesterfield, Dr. Amit Bhandarkar will evaluate your symptoms, review imaging studies (such as MRI or CT scans), and determine if you're a suitable candidate for the procedure.
If endoscopic surgery is right for you, a customized treatment plan will be developed to address your specific condition, whether it's a herniated disc, spinal stenosis, or nerve compression.
Performed under general anesthesia the entire surgery typically takes an hour, allowing patients to walk out the same day with minimal discomfort. Selected patients can be done under local anesthesia as well if preferred.
Endoscopic spine surgery is an excellent option for patients suffering from:
If you're struggling with back pain and seeking a minimally invasive solution with faster recovery, schedule a consultation with Dr. Amit Bhandarkar at S.P.I.N.E. Center Chesterfield today.
+13145573472
https://www.onlinespinecare.com/
Endoscopic spine surgery is transforming the way we treat back and neck pain. By combining advanced technology with minimally invasive techniques, Dr. Amit Bhandarkar provides safer, faster, and more effective spinal care. Don't let chronic pain hold you back—discover the future of spine surgery today!
Click on any section below to learn more about specific endoscopic spine surgery techniques
Interlaminar Endoscopic Spine Surgery (ILESS) is a modern, minimally invasive technique used to treat spinal disorders, particularly in the lumbar spine. It has become increasingly popular due to its ability to offer precise surgical intervention with minimal trauma to surrounding tissues.
This approach leverages endoscopic visualization to access the interlaminar window—the space between the laminae of vertebrae—allowing surgeons to address conditions such as disc herniations and spinal stenosis effectively.
Arthrex Interlaminar Approach Guide
Comprehensive guide on interlaminar approach for endoscopic discectomy procedures.
View Resource
Interlaminar Endoscopy Video
Educational video demonstrating interlaminar endoscopic spine surgery techniques.
The interlaminar approach uses a small skin incision (often under 1 cm) through which an endoscope is inserted to directly visualize and treat spinal pathology. This technique is particularly advantageous for addressing lower lumbar disc herniations (e.g., L4-L5, L5-S1) where the interlaminar space is wider.
During the procedure, surgeons carefully navigate through soft tissues using specialized instruments, avoiding unnecessary damage to muscles or bone. The herniated disc fragment or compressive element is then removed under direct visualization, relieving pressure on the spinal nerves.


| Advantage | Details |
|---|---|
| Minimally Invasive | Reduced muscle and tissue disruption |
| Small Incisions | Typically <1 cm, resulting in faster wound healing |
| Shorter Recovery | Faster return to daily activities compared to traditional open surgery |
| Reduced Pain | Less postoperative discomfort due to muscle preservation |
| Same-Day Discharge | Often performed as an outpatient procedure |
A 2020 study published in Brain & Spine confirmed that interlaminar endoscopic discectomy offers comparable or superior outcomes to traditional microdiscectomy, with significantly reduced surgical trauma and shorter hospital stays [1].
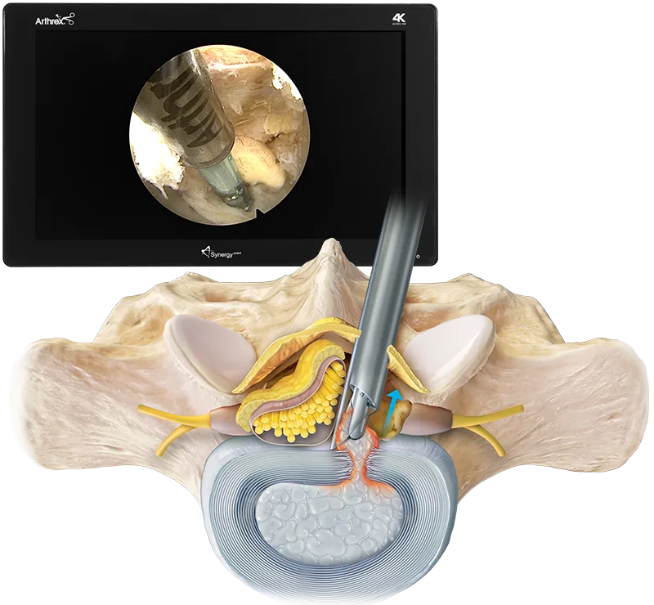
A study by Choi et al. (2016) in Asian Spine Journal showed:
Another comparative analysis by Wang et al. (2021) published in World Neurosurgery concluded that interlaminar endoscopic discectomy was equally effective as microdiscectomy in treating lumbar disc herniation, but with less blood loss and shorter hospital stays [3].
Interlaminar endoscopic spine surgery offers patients a safe, effective, and minimally invasive alternative to traditional spinal procedures. With reduced recovery times and excellent clinical outcomes, it is quickly becoming a preferred choice for treating lower lumbar spine conditions. Patients should consult with a fellowship-trained spine surgeon to determine if they are candidates for this advanced surgical option.

Transforaminal endoscopic spine surgery is a minimally invasive procedure designed to address lumbar disc herniations and related spinal conditions. This technique utilizes a transforaminal approach, accessing the spinal canal through the natural openings (foramina) between vertebrae, allowing for precise intervention with minimal disruption to surrounding tissues.
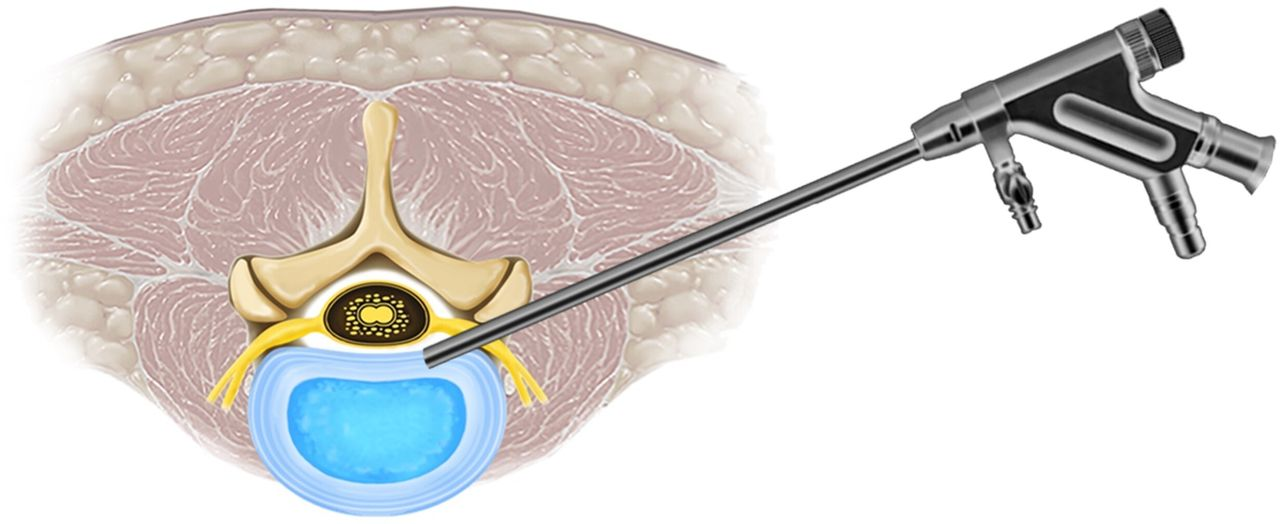
The transforaminal approach involves inserting an endoscope—a thin, flexible tube equipped with a camera and light—through a small incision near the affected area. This allows direct visualization and removal of herniated disc material or decompression of nerve roots. The procedure is typically performed under local anesthesia and is associated with reduced postoperative pain and faster recovery compared to traditional open surgeries.

Transforaminal endoscopic surgery is primarily indicated for:

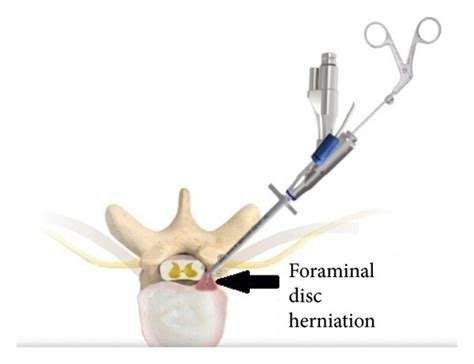
Studies have demonstrated the efficacy of transforaminal endoscopic surgery. For instance, a systematic review comparing this technique to open microdiscectomy found no significant differences in leg pain reduction, overall improvement, re-operation rates, or complications, suggesting it as a viable alternative to traditional methods.
For a comprehensive understanding of the procedure, the following video provides a detailed overview:
Comprehensive guide on transforaminal endoscopic discectomy procedures.
View ResourcePlease note that this video is for educational purposes and may not represent every individual case.
Transforaminal endoscopic spine surgery represents a significant advancement in the treatment of lumbar spinal conditions, offering patients a minimally invasive option with numerous benefits over traditional surgical approaches. As with any medical procedure, consultation with a qualified spine specialist is essential to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
Endoscopic rhizotomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure designed to alleviate chronic back pain by selectively severing nerve fibers responsible for transmitting pain signals from the spine to the brain. This technique offers a targeted approach to pain management, particularly for individuals whose discomfort originates from facet joint dysfunction or arthritis.

The spine's facet joints, which connect adjacent vertebrae, are innervated by medial branch nerves. When these joints become arthritic or inflamed, they can cause significant back pain. Endoscopic rhizotomy involves the use of an endoscope—a thin, flexible tube equipped with a camera and light—to directly visualize and sever these medial branch nerves, thereby interrupting the pain signals. This procedure is typically performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia and sedation. A small incision, often less than a quarter of an inch, is made to insert the endoscope, allowing the surgeon to accurately identify and transect the targeted nerves.

Candidates for endoscopic rhizotomy often include individuals experiencing:

Prior to recommending endoscopic rhizotomy, physicians typically perform diagnostic medial branch blocks to confirm that the facet joints are the source of pain.
Compared to traditional open surgical methods or percutaneous radiofrequency ablation (RFA), endoscopic rhizotomy offers several benefits:
Clinical studies have underscored the efficacy of endoscopic rhizotomy in managing chronic back pain:
For a comprehensive understanding of endoscopic rhizotomy, visual aids can be highly beneficial. The following resources provide detailed illustrations and procedural videos:
Comprehensive guide on medial branch transection procedures.
View ResourceIllustrative overview and intraoperative visualization of endoscopic rhizotomy techniques.
Illustrative Overview: An image depicting the surgical setup and approach for endoscopic rhizotomy, highlighting the minimally invasive nature of the procedure.
Intraoperative Visualization: A video demonstrating the endoscopic technique, showcasing the direct visualization and transection of the medial branch nerves.
Endoscopic rhizotomy represents a significant advancement in the treatment of chronic back pain associated with facet joint pathology. By combining the benefits of minimally invasive surgery with direct nerve visualization, this procedure offers patients effective and long-lasting pain relief. As with any medical intervention, it is essential to consult with a qualified spine specialist to determine the most appropriate treatment plan tailored to individual needs.
Please note that these visual resources are for educational purposes and may not represent every individual case.
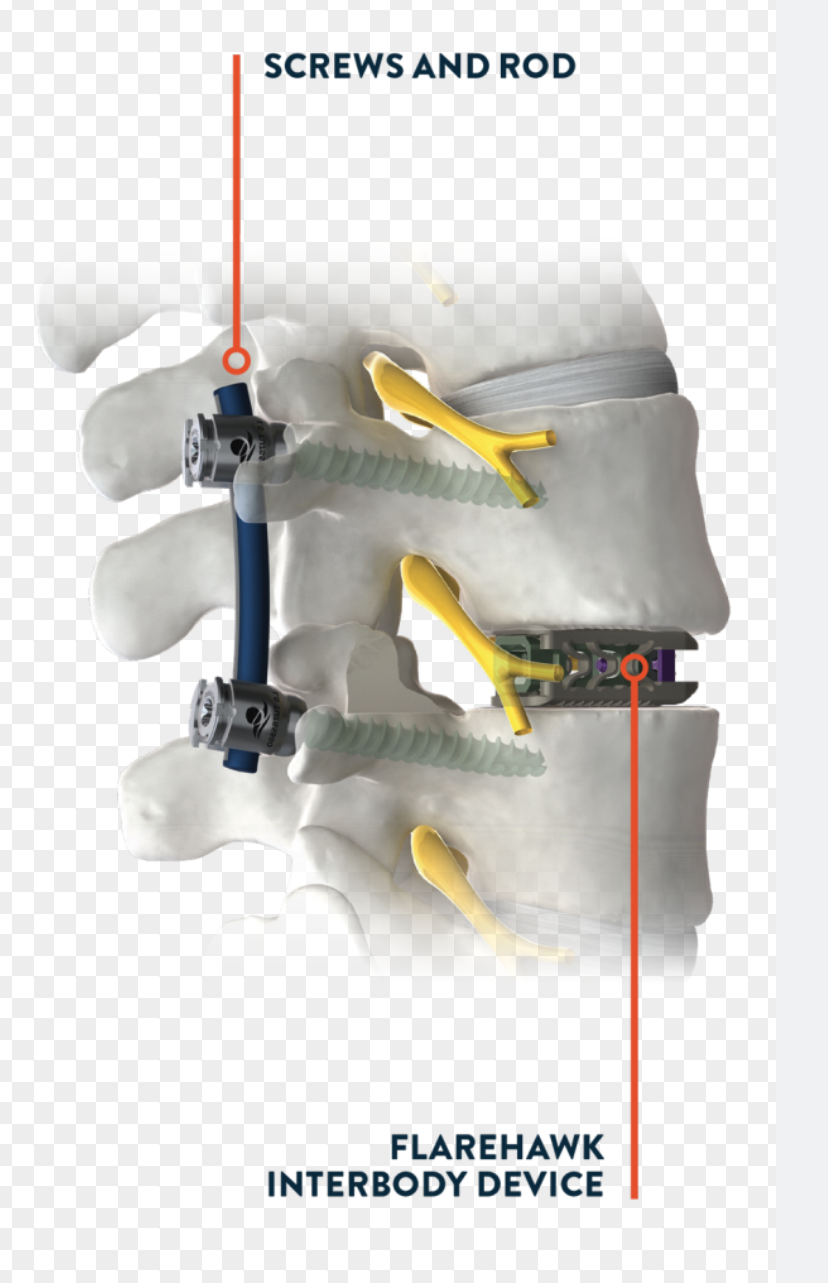
Endoscopic spine fusion represents a significant advancement in minimally invasive spinal surgery, offering patients effective treatment for various spinal conditions with reduced recovery times and minimized surgical trauma.

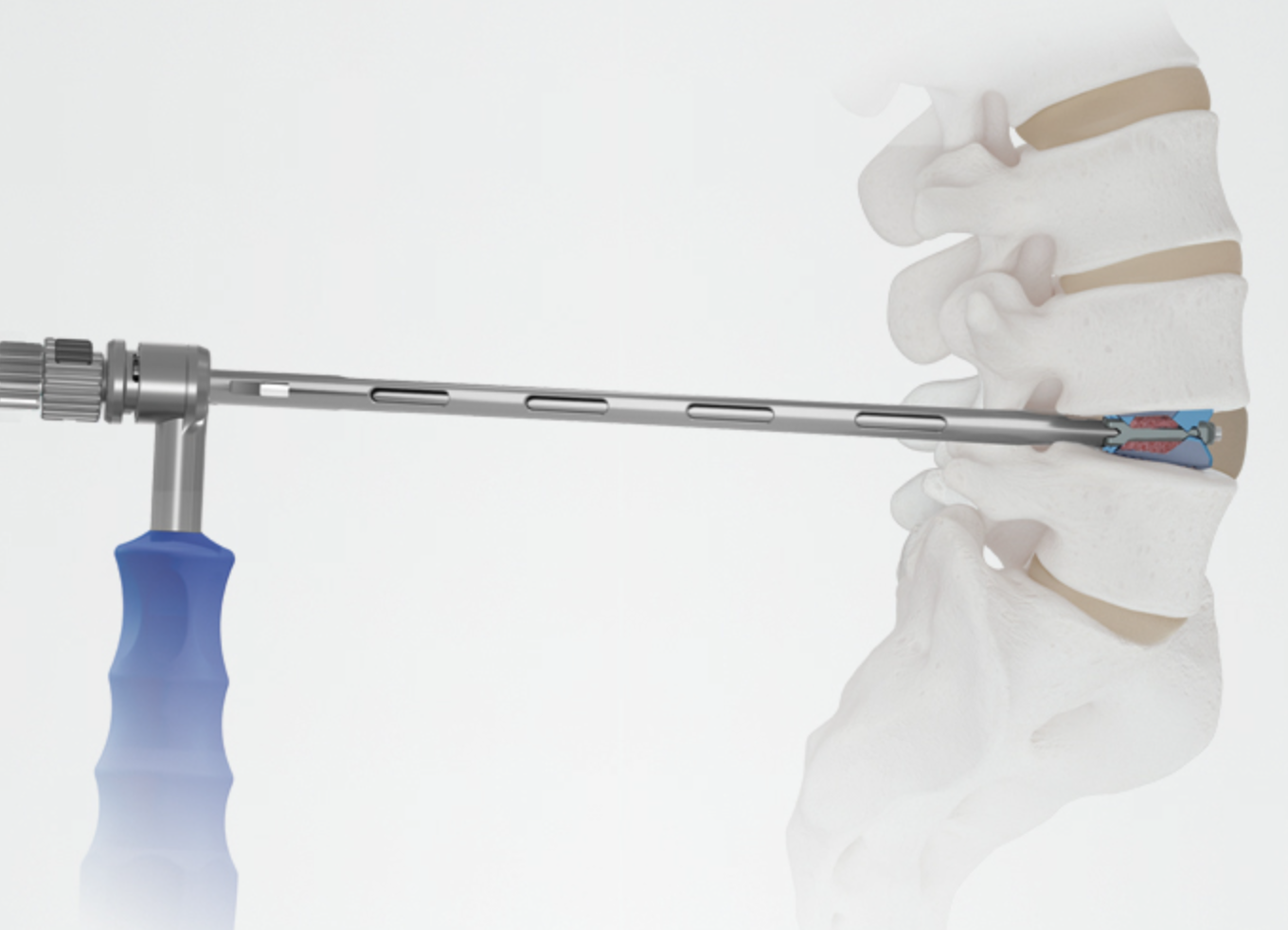
Endoscopic spine fusion is a surgical technique that utilizes specialized instruments and an endoscope—a small, high-definition camera—to access and treat spinal pathology through small incisions. This approach allows for direct visualization of the spinal structures, facilitating precise intervention while preserving surrounding tissues. The primary objective of this procedure is to stabilize the spine by promoting bone fusion between adjacent vertebrae, thereby alleviating pain and restoring function.
For more detailed information, please refer to the comprehensive study on endoscopic spine fusion techniques.
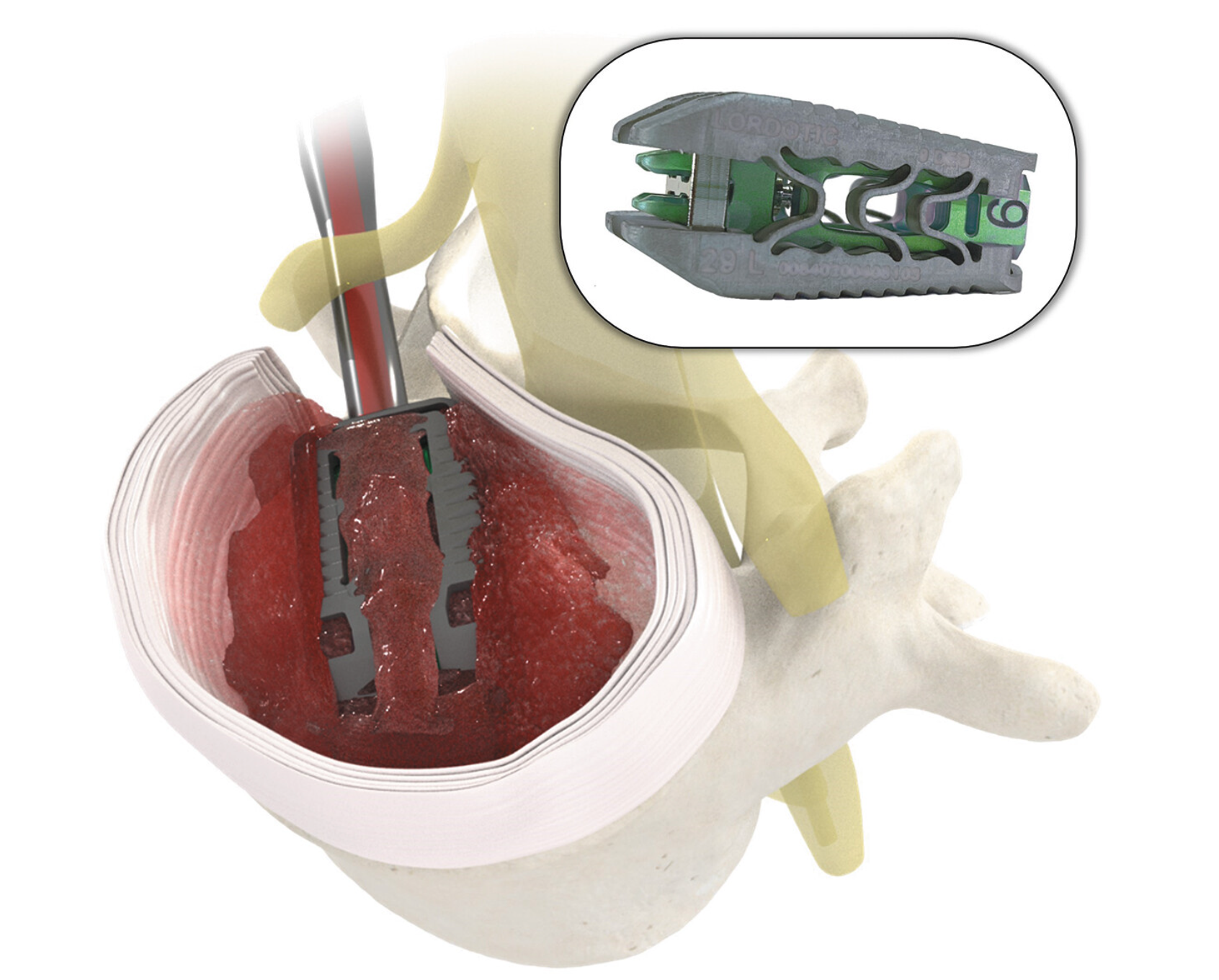
The endoscopic approach offers several benefits over traditional open spinal fusion surgeries:
Recent studies have demonstrated the efficacy and safety of endoscopic spine fusion techniques:
To provide a clearer understanding of the endoscopic spine fusion process, here are some illustrative images and videos:
Advanced expandable technology for spinal fusion procedures.
View TechnologySurgical technique illustrations and intraoperative views of endoscopic fusion procedures.
• Surgical Technique: An illustration depicting the insertion route of the endoscopic system for lumbar endoscopic unilateral laminotomy and bilateral decompression (LE-ULBD).
• Intraoperative View: A photograph showcasing the endoscopic instruments in use during a lumbar interbody fusion procedure.
• Postoperative Imaging: Radiographic images demonstrating the placement and expansion of an expandable cage in a collapsed intervertebral disc, highlighting the restoration of disc height.
Endoscopic spine fusion is an evolving technique that embodies the principles of minimally invasive surgery, offering patients effective treatment options with numerous advantages over traditional methods. As with any surgical procedure, it is essential for patients to consult with their healthcare providers to determine the most appropriate treatment plan tailored to their specific condition.
Please note that these images are for educational purposes and may not represent every individual case.