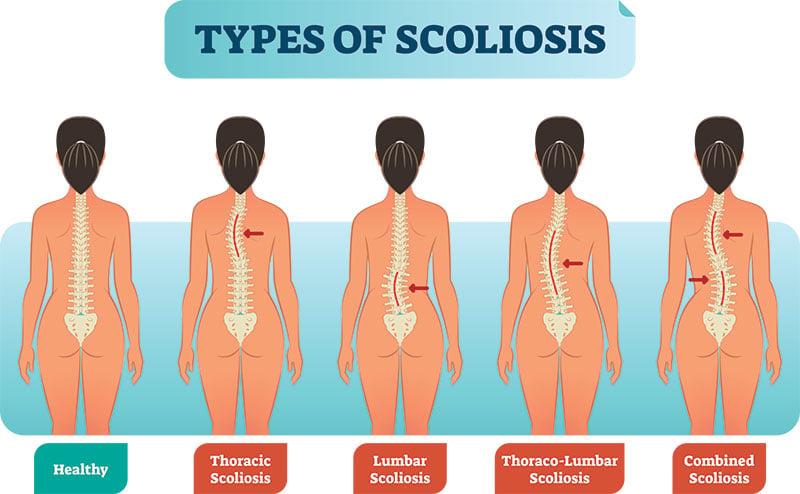
Understanding Mild Scoliosis and Back Pain
Scoliosis is an abnormal sideways curvature of the spine. While a slight forward and backward curve is natural, an S- or C-shaped sideways curve is considered scoliosis.
Scoliosis affects 1-3% of the population, but many cases go unnoticed if the curve is mild. People with larger curves are often diagnosed early and may require bracing or surgery. However, those with low-magnitude scoliosis often remain undiagnosed until they begin experiencing chronic back pain and fatigue in their 30s or 40s.
Common Symptoms of Mild Scoliosis in Adults
Many adults with mild scoliosis develop symptoms after years of normal activity. Common complaints include:
Because the curvature is minor, many patients don’t realize scoliosis is the cause and may be incorrectly treated with pain medications instead of addressing the root biomechanical issue.
How Mild Scoliosis Causes Back Pain
Even though the spinal curve does not usually worsen in adulthood, it still causes imbalances that lead to:
Over time, these imbalances can lead to chronic pain, decreased mobility, and early-onset arthritis.
Diagnosis: How to Confirm Mild Scoliosis
If chronic back pain persists despite standard treatments, a spinal evaluation is necessary. Diagnosis involves:
Once diagnosed, a customized treatment plan can help prevent further pain and functional decline.
Best Treatments for Back Pain from Mild Scoliosis
1. Physical Therapy & Strengthening Exercises (First-Line Treatment)
Since surgery is rarely required, physical therapy is the most effective way to manage pain and improve function.
Important: Just like muscle-building, improvements take months to show results. Many patients give up too soon, expecting quick fixes, which leads to dependence on pain medications.
2. Lifestyle Modifications for Long-Term Pain Relief
3. Additional Pain Relief Methods
If lifestyle changes and therapy alone do not provide enough relief, additional treatments may help:
4. When Is Surgery Considered?
For most patients with mild scoliosis, surgery is not needed. However, in cases where scoliosis has led to secondary arthritis or severe pain unresponsive to treatment, surgical options may be considered.
Expert Scoliosis Care at Chesterfield Spine Center
At Chesterfield Spine Center, Dr. Amit Bhandarkar provides specialized treatment for mild scoliosis and scoliosis-related back pain. Our patient-centered approach includes:
Schedule Your Consultation Today to get expert care and lasting relief from scoliosis-related pain.